Osteoarthritis
What is osteoarthritis?
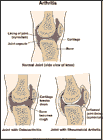
Osteoarthritis, also called degenerative arthritis, is a disease that causes the breakdown of the cartilage in joints. Normally, cartilage acts as a smooth, cushioning material inside joints. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage becomes rough and flaky, and small pieces break off. The bone surface of the joint also becomes rough and irregular. As a result, movement of the joint becomes painful and difficult.
Osteoarthritis occurs most often in weight-bearing joints such as the neck, lower back, knees, and hips. It also often affects the fingers.
Osteoarthritis is three times more common in women than in men. It begins to appear in middle age. By age 60, most people have some osteoarthritis, although it may be too mild to cause symptoms.
How does it occur?
Osteoarthritis is caused by excessive wear on joints. Obesity, bad posture, old injuries, and overuse can all cause extra wear on joints. Heredity also appears to play a role.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
- mild to severe pain in a joint, especially after overuse or long periods of inactivity, such as sitting for a long time
- creaking or grating sound in the joint
- swelling, stiffness, limited movement of the joint, especially in the mornings
- weakness in muscles around the sore joint from lack of use
- deformity of the joint.
How is it diagnosed?
Your health care provider will review your medical history and examine you. Your health care provider may also order blood tests and x-rays. A sample of fluid in the joint may be taken with a needle to confirm the diagnosis.
How is it treated?
The aim of treatment is to keep the joint working by reducing strain on the joint and by relieving pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Generally, acetaminophen is the best medicine for pain relief in osteoarthritis. Older adults should not take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, Nuprin). If acetaminophen does not work, see your health care provider for more guidance and evaluation.
Rubbing anti-inflammatory or deep-heat creams over the arthritic joint can sometimes be helpful. Putting an ice pack on your the joint once or twice a day can also help relieve pain. Your health care provider may inject steroids into the painful joint.
If you are overweight, your health care provider may recommend that you lose weight by eating fewer calories, by increasing your physical activity, or both.
Physical and occupational therapy can help you have normal movement again. Regular gentle exercise is very important for controlling osteoarthritis.
Sometimes severely damaged hips and knees are surgically replaced.
How long will the effects last?
Unfortunately, osteoarthritis is a lifetime disease that can worsen over time. Avoiding repeated injury to your joints can help, but damaged cartilage cannot repair itself.
How can I take care of myself?
Although no one yet knows how to prevent osteoarthritis, you can help prevent symptoms by following these guidelines:
- Keep your joints in good working order. Stay fit. Do any exercises recommended by your health care provider or physical therapist for posture, muscle strength, and joint mobility. Daily moderate exercise is much better for your joints than occasional strenuous exercise. Walk a little each day if you can. Be sure to wear comfortable, well-cushioned walking shoes. Otherwise, you can exercise while sitting down or go swimming. The water in a warm swimming pool can help support your weight while you exercise, and the warmth helps improve joint movement.
- Protect your joints by doing warm-up exercises before strenuous activity.
- Use a knee pad to protect your knees when you are kneeling.
- Take the medicine your health care provider recommends for controlling your osteoarthritis.
- Keep your body healthy by eating a healthy, varied, low-fat diet.
- Follow your health care provider's recommendations for weight control.